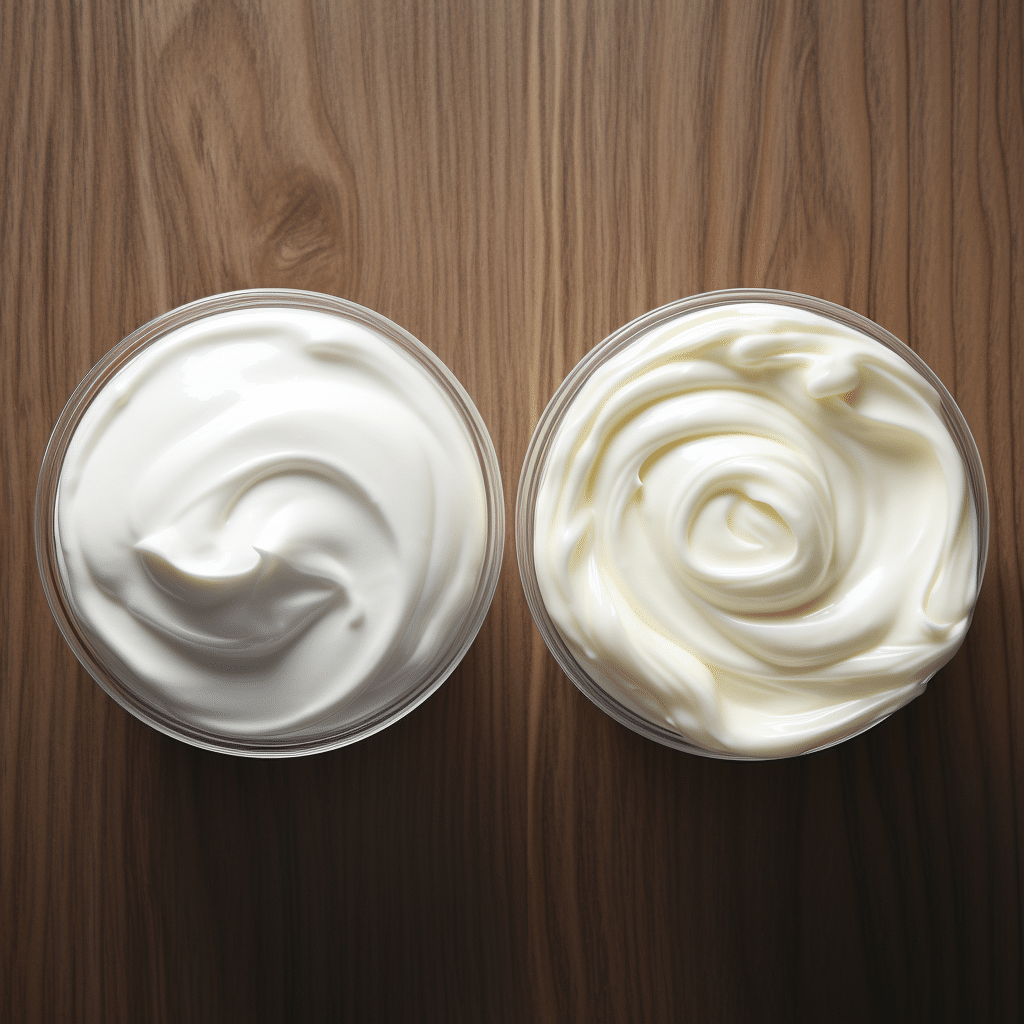
Crème Fraiche vs Heavy Cream: Differences and Uses
Creme fraiche and heavy cream are two popular dairy products used globally. They have many different uses in culinary and make a superb addition to dishes like sauces. However, they are different, and although you can sometimes use one instead of another, you can’t always use them interchangeably. So, what are they, and what makes them different? Here’s a look at crème Fraiche vs. heavy cream discussing what they are and their differences.

Crème Fraiche vs Heavy Cream
Both crème Fraiche and heavy cream are obtained from dairy milk. Crème Fraiche is cultured heavy cream, while heavy cream is buttermilk.
Differences Between Creme Fraiche And Heavy Cream
Creme fraiche and heavy milk are made from the top milk layer, which separates when milk is heated. Heavy cream is fatty, constituting 36% to 40% fat, whereas crème Fraiche is less fatty, consisting of up to 30% fat. Besides fat content, other differences include:
How They Are Produced
Although there are many ways of making heavy cream at home, the whole production process is pretty simple. During production, milk is heated until the top layer of fat separates from the rest of the milk – the less dense and fluid milk part. Once the fat layer separates, it is skimmed off, leaving the watery part. And there you have your buttermilk.
On the other hand, crème Fraiche is obtained from heavy cream. Cultural bacteria are added to the heavy cream during production to ferment it. The cultured bacteria are milk bacteria which comprise Lacto bacteria. These bacteria bring about the fermentation process, which can take place between 12 to 24 hours, depending on the thickness of the cream. Once fermented, the end product has a different taste, texture, and consistency from the original heavy cream.
How They Taste
Taste is a crucial aspect when differentiating between crème Fraiche and heavy cream. Crème Fraiche is a by-product of fermentation. As such, it has a strong, tangy, slightly sour, and a bit savory flavor. This limit its uses in various dishes.
As for heavy cream, this one has a more neutral taste and can be used in sweet and savory dishes. Besides having a neutral flavor, heavy cream also has a rich, creamy, and buttery taste, making it a great addition to dishes that require a creamy touch.
Their Texture
Regarding texture, crème Fraiche is creamy, relatively thicker, and curdles. Its consistency resembles thick yogurt or mayonnaise.
On the other hand, heavy cream is less thick than crème Fraiche but fattier. Heavy cream’s thickness and consistency largely depend on the amount of buttermilk present in the top layer of the milk.
As a step guide, crème Fraiche is thicker than heavy cream. However, it’s not as heavy as heavy cream. And heavy cream is fattier but not as thick as crème Fraiche. Heavy cream can be considered more of a thick liquid than stable cream.
Culinary Uses
The unique tastes of crème Fraiche and heavy cream make them ideal for various dishes. Creme fraiche has a tangy, slightly acidic, and savory flavor. This makes it a perfect fit for use as a salad dressing, sauce thickener, roasted meat topping, or on top of fruit salads with a bit of sugar. Creme fraiche is also great when used in omelets or smeared on top of baked goods.
On the other hand, heavy cream is rich, creamy, buttery, and has a neutral taste. For this reason, it is best used as a thickener or added to custard desserts. Heavy cream also works well when added to any dish that requires creaminess, DIY cheese like paneer and ricotta, and any dish that needs the buttery richness of heavy cream.
Nutritional Information
Both crème Fraiche and heavy cream are high in fats and calories. They should, therefore, not be consumed regularly and instead treated as an occasional treat.
Crème Fraiche contains fewer amounts of saturated fats compared to heavy cream. Two tablespoons of this milk-based crème provide 35% of your daily fat needs. Fats are an essential nutrient in the body, providing insulation, transporting fat-soluble vitamins, producing hormones, and promoting healthy skin. But as with anything, moderation is critical; as too much of it can harm your health.
Although crème Fraiche is high in fat, it doesn’t contain many vitamins and minerals. But it has considerable amounts of calcium necessary for healthy bones and teeth. Crème Fraiche is also low in carbs, making it perfect for individuals on a weight loss program or low-calorie diet.
Another thing to note is that crème Fraiche is produced through fermentation of heavy cream using Lacto bacteria. Lacto bacteria are gut-friendly bacteria that promote gut health and improve digestion. But remember to consume it in moderation as too much bacteria, even good bacteria, can disrupt the natural balance of the gut’s microbe composition.

Heavy cream is very high in saturated fats and calories than creme fraiche
It may not be great for individuals watching their calories or those struggling with heart diseases. But besides calories and fats, heavy cream has numerous health benefits over crème Fraiche.
One, heavy cream is a rich source of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K. These vitamins all play a crucial role in the body, improving vision, strengthening bones, fighting free radicals, and enhancing blood clotting processes. Heavy cream also contains minerals like calcium, phosphorus, and chlorine, which are vital for strong bones and normal blood osmotic pressure.
Heavy cream is low in carbs and contains considerable amounts of proteins for muscle building, higher than crème Fraiche. But like crème Fraiche, heavy cream should be consumed in moderation. As a step guide, don’t overdo the two. Use them sporadically and in low amounts. Otherwise, you risk affecting your health.
Conclusion
Creme fraiche is excellent for foods that need more character, zest, or ting. So, use it with baked goods, fruit salads, roasted meat topping, salad dressing, or in a pan sauce.
Heavy cream is your go-to anytime you need extra thickness and creaminess. So use it as a thickener, sauce base, DIY cheese, or in custard desserts.